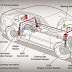
1) Sports Cars-
Sports cars are the perfect example of best automobile engineering, sports cars are usually two-seater small cars that are designed for quick response to move fast for spirited performance and nimble handling. They are brutal acceleration (0-100kmph in 2.3 sec Bugatti Chiron) and can achieve very high speed (436kmph hennessey venom GT). Some example of sports cars are Nissan GTR, Lamborghini Veneno, and Maserati Alfieri, Koenigsegg Agera etc.
2) Muscle Cars-
A type of car designed for power and high performance, these cars have powerful engine, mostly V-8 and above with 2-door. Apart from this their performance, their look is muscular and aggressive. They are good for street driving and occasional drag race. Some common example are Ford Mustang, Chevrolet Camaro, Dodge charger etc.
3) Sedan or Saloon type Cars-
Sedan is a passenger car that has two rows of seats, adequate passenger space in the rear compartment for adult passengers and large trunk cargo compartment in rear. In sedan, a four or more people can travel and has a fixed roof that is full height up to the rear window with two pillar to join roof and window. The word sedan is taken from Italian sedia “chair” in that closed chair one person can sit. Some common examples are Porsche Panamera, Audi A8, Hyundai Verna, etc.
4) SUVs type Cars-
A sport utility vehicle (SUV) is an estate car mostly available in four wheel drive to drive on-road and off road, having large passenger carrying space. If you wish to further categorize the SUV car they are sub divided in many type as per their size like Compact SUV, Mid-sized SUV, Full sized SUV etc. Some popular SUV’s are BMW X4, Porsche Macan, Maserati Levante, Mahindra Scorpio, Toyota Fortuner etc.
5) Multi-utility vehicles MUVs-
Usually based on either a mid-sized car or minivan platform. Usually two-wheel drive "people movers". They have higher ceilings, more storage than a sedan, some of the utility of a SUV with a similar ride, though from a construction standpoint not as robust. They are designed for passenger comfortable, safety and fuel economy. Examples are Toyota sienna, Toyota innova, Honda Mobilio, Maruti ertiga etc.
6) Hatchback-
Passenger cabin with integrated cargo space. Its rear cargo space is accessed by way of a gate or hatch that is hinged at the top of the vehicle, above the rear window It has no more than three pillars A, B and C. Examples Volkswagen polo, Hyundai i20, i10, Maruti Suzuki alto, Nissan Datsun, Honda brio etc.